Pro rata rebates
Pro rata means proportional. In Rebates, the Pro Rata option in a rule is suitable if you are paying or claiming the rebate on a yearly basis, but you want to see how rebates are likely to track for the whole year when you are only part-way through the year. You might refer to this as annualization or annualizing.
If you don’t use the Pro Rata option and you run a calculation during the year, you’ll only know the rebate amount up to that point in time. You won't know what the rebate will be at the end of the year; you’ve no idea if it’ll be above or below your target. If you do use the Pro Rata option, you’ll get a forward-looking calculation that will predict what the rebate will be at the end of the year.
Pro rata rebate rules help you overcome the challenge of calculating and forecasting the financial impact of yearly rebates at a particular point during the year by allowing you to anticipate the yearly rebate. Such knowledge influences purchase decisions (receivable rebates), provides the expected cash outlay (payable rebates), and helps you to keep track of your budgets.
The forecasted rebate amount will fluctuate each time you run the calculation. For example, if you get $12,000 in January and run the calculation then, based on the Pro Rata option, it’ll assume you’re going to get $12,000 each month and apply the bracket parameters to predict the final rebate amount. If you only get $3,000 in March and run the calculation amount, the predicted final rebate will be different. Whether you run a calculation each month or over a number of months (such as each quarter), the final rebate will be the same. However, monthly calculations are typically preferred by finance departments.
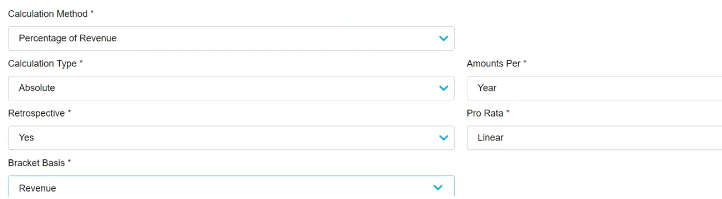
In the rebate rule setup, the Pro Rata setting is available when the Calculation Type = Absolute, the bracket Amounts Per = Year, and Retrospective = Yes.
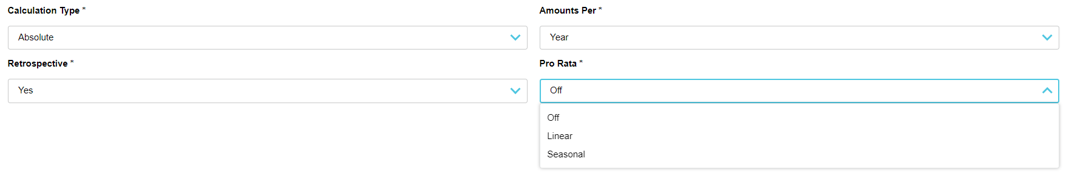
This conditional availability is illustrated in the following diagram.
Pro rata options
There are three pro rata options:
Off: This is the default setting; the pro rata function is NOT used when calculating the rebate amount throughout the year.
Linear: This is the standard method for calculating a rebate over a year (12 months).
Each month is weighted equally to estimate the bracket in which a rebate is likely to fall by the end of the year. Your actual results are multiplied by the number required to make 12 months, then the brackets are applied accordingly to calculate the results.
This option is suitable when it is likely your targets will not be met until late in the year. It allows you to estimate the monthly or quarterly rebate level that you will be paying or receiving.
Seasonal: This method calculates pro rata projections based on a seasonality calendar.
Each month is weighted differently when calculating the results. For example, suppose in January you expect only 5% of yearly sales, whereas in July you expect 20% of all sales.
This option is suitable if your business has seasonal variations, as it allows you to factor in that seasonality and, therefore, estimate the rebate amount more accurately. For example, if you have a slow start to the year, the first months of the year will lead to underestimations about the performance, and if you used the linear method, the bracket applied might not be representative of the year overall; the results would be skewed.
If you have more than one seasonal calendar, the Calendar setting displays, from which you need to select the applicable calendar.
Watch this Phocas Academy video: Pro rata rules
Example: How the linear pro rata rebate is calculated
Suppose you have set up a rebate rule like this:
With these brackets:
0
100,000
1%
100,000
200,000
2%
200,000
300,000
3%
300,000
400,000
4%
400,000
1,000,000
5%
If the transaction amount for January was 33,927.40, then according to these brackets, without pro-rata you’d get a 1% rebate on that amount. But it is a pro-rata rebate, and you are on track to meet the 400,000 to 1,000,000 bracket for the full year, so you get the 5% rebate.
Now suppose that you continue for the next two months, but in March there are no sales at all:
January
33,927.40
5%
1,696.37
February
52,359.37
5%
2,617.97
March
0
4%
-862.87
Total
86,286.77
4%
3,451.47
In February, you continue to get the 5% rebate. But in March, based on the transaction amounts so far, the overall rebate will now be only 4%. So the pro-rata rebate for that month is negative to adjust for the overestimate in the previous months.
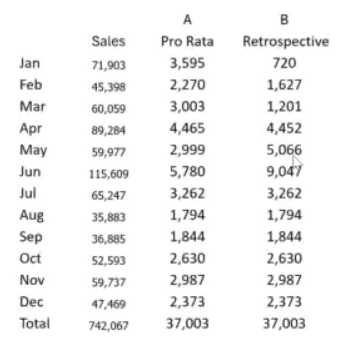
Pro rata versus Retrospective: application and results
This table contrasts the calculation of a rebate under two different bracket conditions: Pro Rata (column A) and Retrospective (column B) over the course of a year. Note how each method yields different monthly results, but both methods yield the same year-end result. You can see that the Pro Rata method provides a more precise tracking of the rebate.