Retrospective rebates
You might be unfamiliar with the term retrospective when thinking about rebates. However, retrospective rules follow the standard understanding of the word. These rules look back and perform an action on past events, as they are typically calculated after a specific period has passed. This approach contrasts with the pro rata rules that look forward.
In the context of rebates, a retrospective is an adjustment. The highest accrued rebate is retrospectively applied to the applicable transactions in the specified date range to adjust their rebate value. This description can be broken down into the following points:
The highest accrued rebate is the highest bracket that the cumulative total hits. This is the starting point for all retrospective rebates.
The applicable transactions are those that meet the condition.
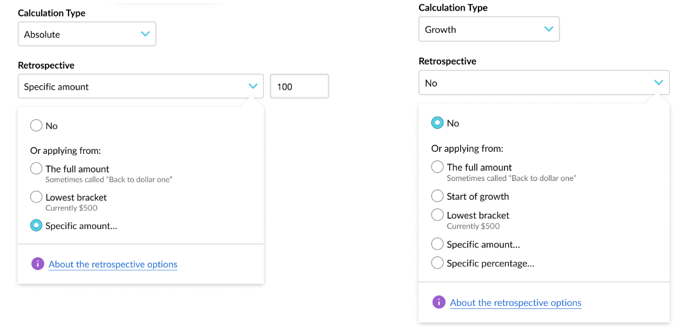
The condition is the Retrospective setting in the rule. It’s the method by which you want to apply the adjustment, which can be a threshold, such as from the start of their lowest bracket value, from the start of positive growth compared to their previous period, or from a specific amount or percentage. Alternatively, the condition can include all the transactions in the calculation period.
The specified date range is the calculation period.
The calculation results for retrospective rebates look similar to those for non-retrospective rebates in that there is a line for each bracket that is met, but there is an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.
Why use retrospective rebates?
The general goal of retrospective rebates is to incentivize large sales or purchases, long-term commercial relationships, or consistent growth year on year. Applying the highest accrued rebates to the applicable transactions gives the customer or vendor a higher rebate rate across all their sales for that period. Specific use cases are given for each method below.
Retrospective rebate methods
There are several ways to apply retrospective rebates, depending on whether the rule calculation type is Absolute or Growth.
No
✓
✓
Full amount
✓
✓
From the start of growth
✓
From the lowest bracket
✓
✓
From a specific amount
✓
✓
From a specific percentage
✓
In the rule setup, click the Retrospective dropdown list and select the required method.
No retrospective rebates
When the Retrospective setting is set to No, there are no retrospective rebates; the calculated rebates are not adjusted. The bracket percentage or value is only applied to the transactions that have met the criteria for that bracket. This method works like income tax brackets.
The full amount
Any rules with the previous Retrospective setting of Yes will have this method selected by default.
The full amount retrospective method is available for absolute and growth rules. It applies the highest accrued bracket to all the transactions in the calculation period, including negative transactions. This type of rebate application is commonly referred to as a back-to-dollar-one rebate because the rebate is not just applied to the transactions in the highest accrued bracket but to all the transactions in that period, right back to the first dollar earned or spent.
This method is available for absolute and growth rules. With absolute rules, you’re dealing with an absolute amount, whereas with growth rules, you’re dealing with the rate of growth in the current period compared to that in the previous period.
This method is suitable when you want to pay or receive the highest rebate accrued to encourage a larger volume of sales or purchases.
Watch this Phocas Academy video: Retrospective rules (using the full amount option)
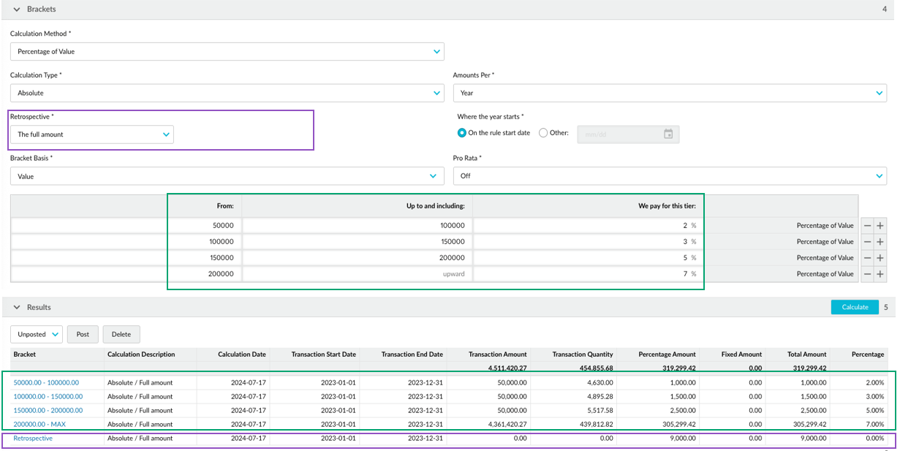
Example 1: Absolute rebate rule with retrospective on the full amount
Suppose an absolute rebate rule has four brackets (2%, 3%, 5%, and 7%), and the cumulative total for the calculation period hits the highest bracket (7%).
In the calculation, the brackets are applied to the transactions as usual, and a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions that hit a lower bracket. This means:
The transactions that hit the first bracket initially get a 2% rebate, but with the retrospective adjustment, they get an additional 5% (7-2=5).
The transactions that hit the second bracket initially get a 3% rebate, but with the retrospective adjustment, they get an additional 4% (7-3=4).
The transactions that hit the third bracket initially get a 5% rebate, but with the retrospective adjustment, they get an additional 2% (7-5=2).
The transactions that hit the highest bracket get no retrospective adjustment as they already get the 7% rebate.
In summary, all the transactions, including those that didn’t hit the first bracket, get the highest rebate of 7%. In other words, the retrospective is applied to the full amount, right back to dollar one.
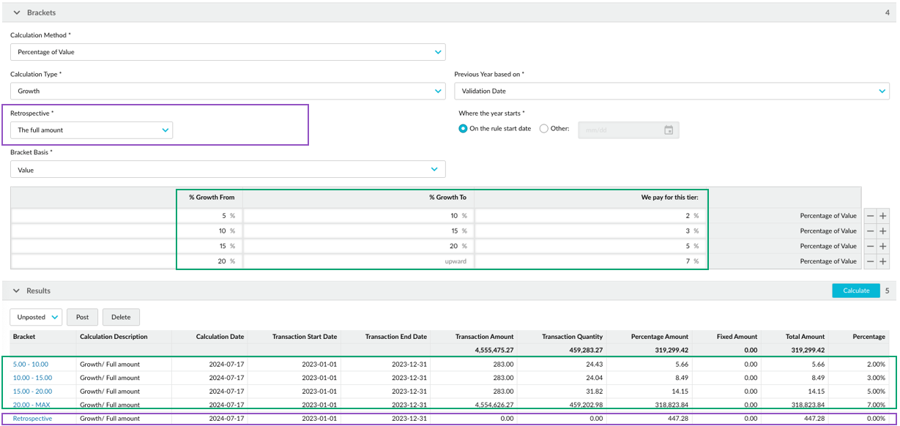
Example 2: Growth rebate rule with retrospective on the full amount
Using the same bracket setup as in example 1 above, but this time in a growth rebate rule, suppose you have the following information:
Previous period: Jan 2022 to Jan 2023, cumulative total of sales is 3,648,000.
Current period: Jan 2023 to Jan 2024, cumulative total of sales is 4,561,000
When sales in the current period are compared to the previous period, the growth is 25%, which is in the highest bracket (7%).
In the calculation, the brackets are applied as usual, then the retrospective adjustment is applied to all the transactions, including those that didn’t hit the first bracket, to give them highest rebate of 7%. In other words, the retrospective is applied to the full amount, right back to dollar one.
In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for that retrospective adjustment.
From the start of growth
The start of growth retrospective method is available for growth rules only. As its name suggests, the condition (threshold) is the start of growth. It applies the highest accrued bracket to all transactions in the calculation period that contribute to positive growth from the previous period.
If the previous period doesn’t exist, the cumulative total for the previous period is considered 0, so every transaction in the current period is eligible for the retrospective rebate.
This method is suitable, for example, in payable rebates, when you want to use brackets as a baseline and reward customers for any increase in sales. But you don’t want to pay any retrospective rebates if there’s no growth in the current period.
Example: Growth rebate rule with retrospective from the start of growth
This example uses the same scenario as the full amount section above, where the current period’s cumulative total represents 25% growth, meeting the highest bracket (7%). The cumulative total of transactions in the current period above the previous period’s total (3,648,000) shows positive growth, making them eligible for the retrospective rebate.
In the calculation, the brackets are applied as usual, then the retrospective adjustment is applied to all the transactions from the start of the growth onwards, to give them the highest rebate of 7%. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for that retrospective adjustment.
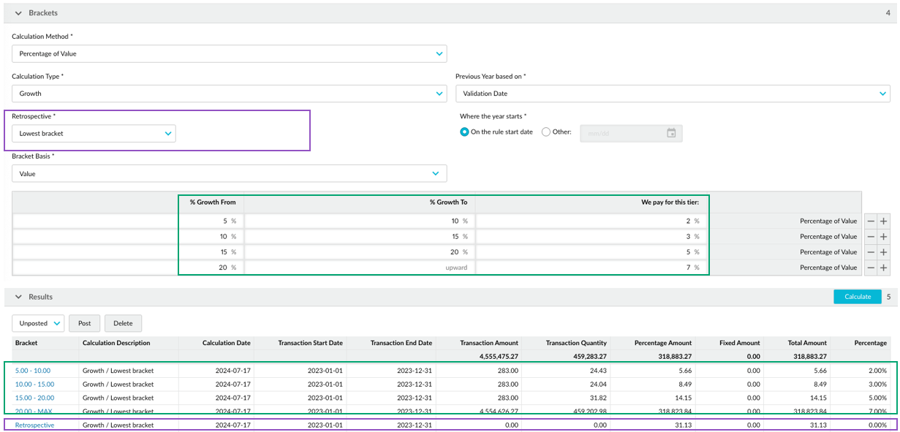
From the lowest bracket
The lowest bracket retrospective method is available for absolute and growth rules. The condition (threshold) is the lowest bracket in the rule setup. Therefore, when applying the highest accrued bracket to the transactions in the calculation period, it doesn’t include transactions lower than the first bracket. Unlike the full amount method, not all transactions get the retrospective adjustment.
This method is suitable, for example, in payable rebates, when you want to use brackets as a baseline and encourage customers to spend more. But you don’t want to pay any retrospective rebates for transactions below the first bracket. It’s not enough for customers to spend more; you want customers to spend a minimum amount or grow their spending by a minimum percentage. The lowest bracket is the minimum requirement for the rebate; anything less than that is not eligible.
You can then clone the rebate rule for other customers or scenarios then change the brackets as required.
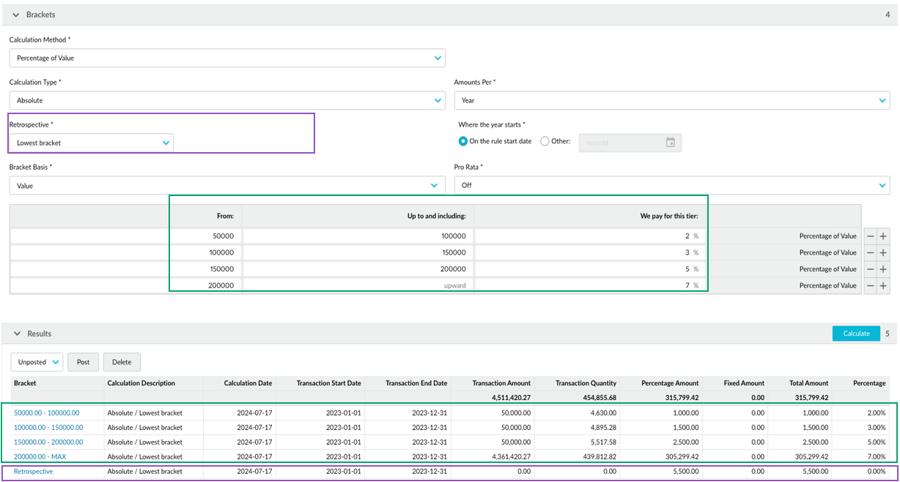
Example 1: Absolute rebate rule with lowest bracket retrospective
This example uses the same scenario as the full amount > absolute example above, where the cumulative total for the calculation period hits the highest bracket (7%). The lowest bracket is from 50,000 and it gets a 2% rebate.
In the calculation, the brackets are applied to the transactions as usual. Then a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions in and above the lowest bracket. Transactions below that bracket (less than 50,000) are ignored. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.
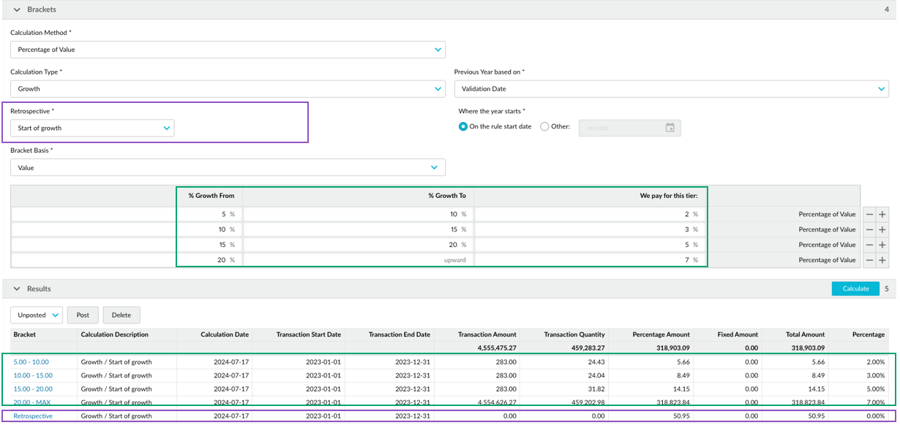
Example 2: Growth rebate rule with lowest bracket retrospective
This example uses the same scenario as the full amount > growth example above, where the cumulative total for the calculation period hits the highest bracket (7%). The lowest bracket is growth from 5% compared to the previous period, and it gets a 2% rebate.
In the calculation, the brackets are applied to the transactions as usual. Then a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions in and above the lowest bracket. Transactions that fall below that bracket (less than 5% growth) are ignored. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.
From a specific amount
The specific amount retrospective method is available for absolute and growth rules. The condition (threshold) is an amount specified by you in the rule setup. Therefore, when applying the highest accrued bracket to the transactions in the calculation period, it doesn’t include transactions with a cumulative total lower than that amount. Unlike the full amount method, not all transactions get the retrospective adjustment. If the specified amount is higher than a bracket amount, the transactions that fall into brackets lower than that amount will only get the bracket rebate, not the adjustment.
This method is suitable, for example, in payable rebates, when you want to use brackets as a baseline and encourage customers to spend more than a specific amount. You don’t think it’s fair to pay a high rebate amount for transactions with a cumulative total below that amount. You can then clone the rebate rule and set an individual threshold for each customer.
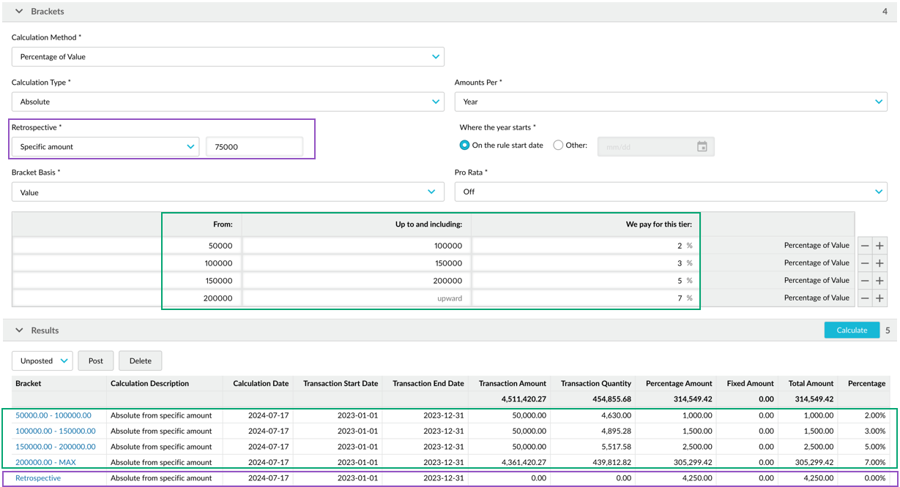
Example 1: Absolute rebate rule with retrospective on a specific amount
Suppose you negotiated a contract with a customer that says they’ll earn a rebate for sales over 75,000 in a calendar year. The rebate rule has four brackets (2%, 3%, 5%, and 7%), and the customer’s cumulative total for the calculation period hits the highest bracket (7%).
In the calculation, the brackets are applied as usual. Then a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions with a cumulative total above 75,000. Transactions with a cumulative total below that amount are ignored. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.
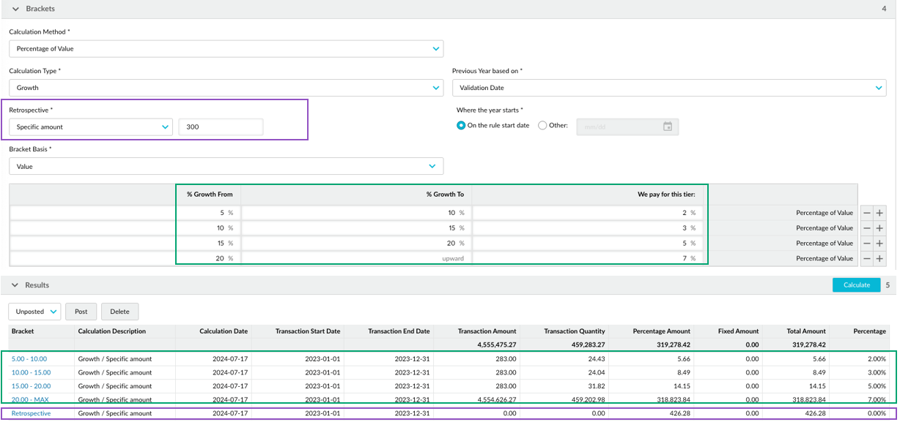
Example 2: Growth rebate rule with retrospective on a specific amount
In this example, the specific amount is 300. The rebate rule has four brackets (2%, 3%, 5%, and 7%), and the customer’s cumulative total for the calculation period hits the highest bracket (7%).
In the calculation, the brackets are applied to the transactions as usual. Then a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions with a cumulative total above 300. Transactions with a cumulative total below that amount are ignored. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.
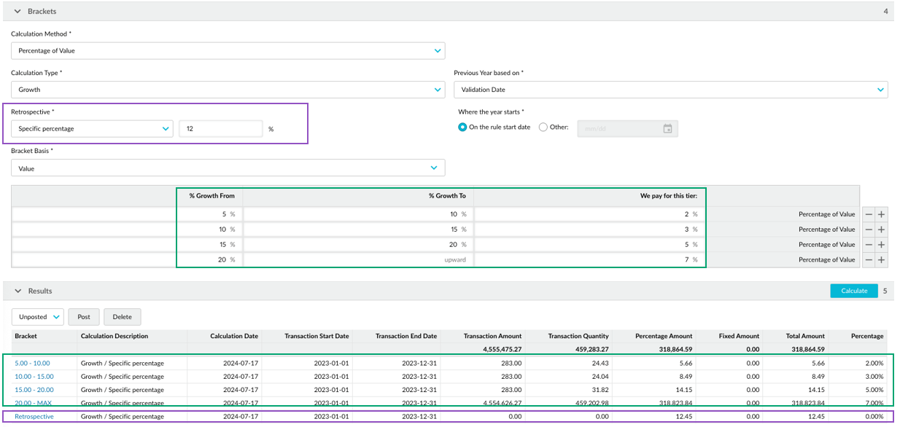
From a specific percentage
The specific percentage retrospective method is available for growth rules only. It works the same as the specific amount method above but uses a specified percentage of growth instead of an amount. The condition (threshold) is a percentage specified by you in the rule setup. Therefore, when applying the highest accrued bracket to the transactions in the calculation period, it doesn’t include transactions with a cumulative total lower than that percentage of growth. Unlike the full amount method, not all transactions get the retrospective adjustment. If the specified growth percentage is higher than a bracket growth percentage, the transactions that fall into brackets lower than that percentage will only get the bracket rebate, not the adjustment.
This method is suitable, for example, in payable rebates, when you want to use brackets as a baseline and encourage customers to grow their spending by a specific percentage. You don’t think it’s fair to pay a high rebate amount for transactions with a cumulative total below that growth rate. You can then clone the rebate rule and set an individual threshold for each customer.
Example: Growth rebate rule with retrospective on a specific percentage
In this example, the current period’s cumulative total represents 25% growth, meeting the highest bracket (7%). In the calculation, the brackets are applied to the transactions as usual. Then a retrospective adjustment of 7% is applied to all transactions with a cumulative total above 12%. Transactions with a cumulative total below that percentage are ignored. In the calculation results, there’s an additional line for the retrospective adjustment.